Website owners and SEO specialists scanning server logs in late 2025 are noticing an unusual new entry:
ChatGPT%20Atlas/2025xxxx CFNetwork/xxxx.x Darwin/xx.x.xThis is not a bot. It’s the user-agent of ChatGPT Atlas, OpenAI’s new AI-powered browser now rolling out globally for Mac OS Users on paid plans.
Note: As per experimentation with my own website and data from my server logs, the above user agent is only accessing my Favicon and Logo.
When using Atlas browser, the rest of the content and web-page is accessed through the below user agent which appears to be a chrome instance. This would make it hard to track and block ChatGPT Atlas browser. (Source: chrisrcook.com)
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_3) AppleWebKit/123.45 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/142.0.0.0 Safari/537.36While the AI industry is discussing Atlas for its “agent mode” and automation features, very few developers or SEOs understand what this user-agent means when it shows up in access logs. This article explains it in a clear, technical but concise way as much as possible.
What Exactly Is ChatGPT Atlas?
ChatGPT Atlas is a standalone browser built by OpenAI that merges web browsing with live AI assistance. Instead of switching between a browser and ChatGPT, users browse the web inside ChatGPT.
As more users adopt Atlas, your server logs will begin showing requests coming from this new browser.
What the User-Agent Actually Means
When you see a string like this:
ChatGPT%20Atlas/20251112345678123 CFNetwork/1234.123.123 Darwin/12.3.4
Here’s the technical breakdown:
- ChatGPT%20Atlas → A normal space-encoded identifier (
%20= space)
The request came from the ChatGPT Atlas browser, not Chrome, Safari, or Firefox. - Build Number (20251112345678123) → This is a unique version/build identifier.
It represents the internal build OpenAI is running. - CFNetwork/xxxx → Apple’s networking framework used by macOS apps.
This confirms the user is browsing through the macOS version of ChatGPT Atlas. - Darwin/xx.x.x → Darwin kernel version, the Unix foundation of macOS.
Note: It’s not clear yet what’s the role of this user agent as I was unable to find any information on this user agent on the internet except the below one.
If you want to know more about this user agent, go to useragents.io
Important for SEOs:
✔ It is not a crawler.
A Unique Feature: How Atlas Displays Search Results
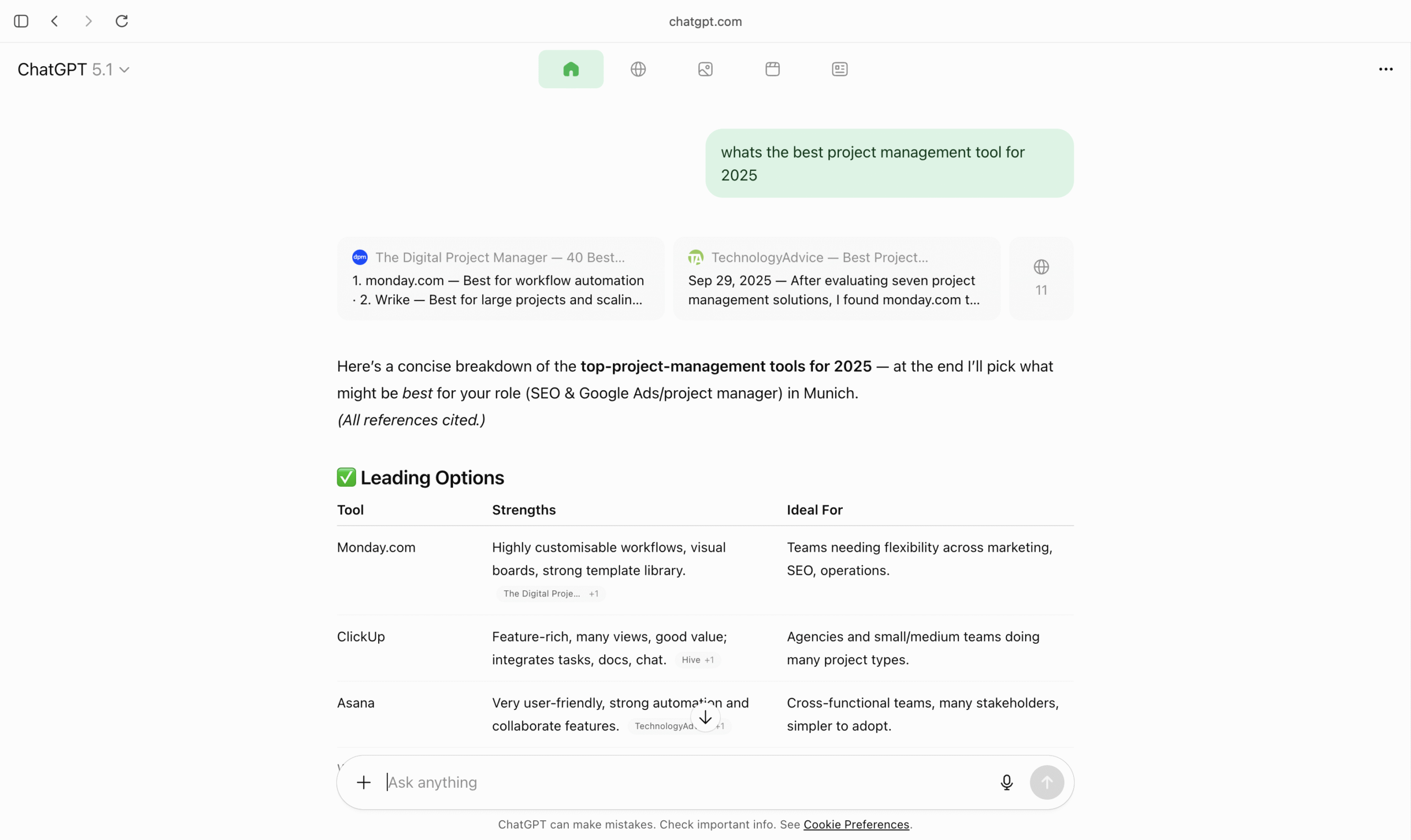
One of the biggest UX differences between using ChatGPT in Atlas and in traditional browsers: the way search results are displayed.
1. AI-Generated Answer With Direct Citations (Top Section)
When a user asks something (e.g., “best project management tool for 2025”), Atlas instantly generates a structured answer.
At the top, it shows:
- Key points
- Summaries
- A neatly formatted table
- Clickable source cards from the web-pages it used (This is not shown if you use ChatGPT in other browsers such as Chrome or Safari). However, this source card will only show up up ChatGPT uses web based retrieval for the prompt. If the web-based retrieval is not used then clickable source card with the below mentioned featured will not show up.
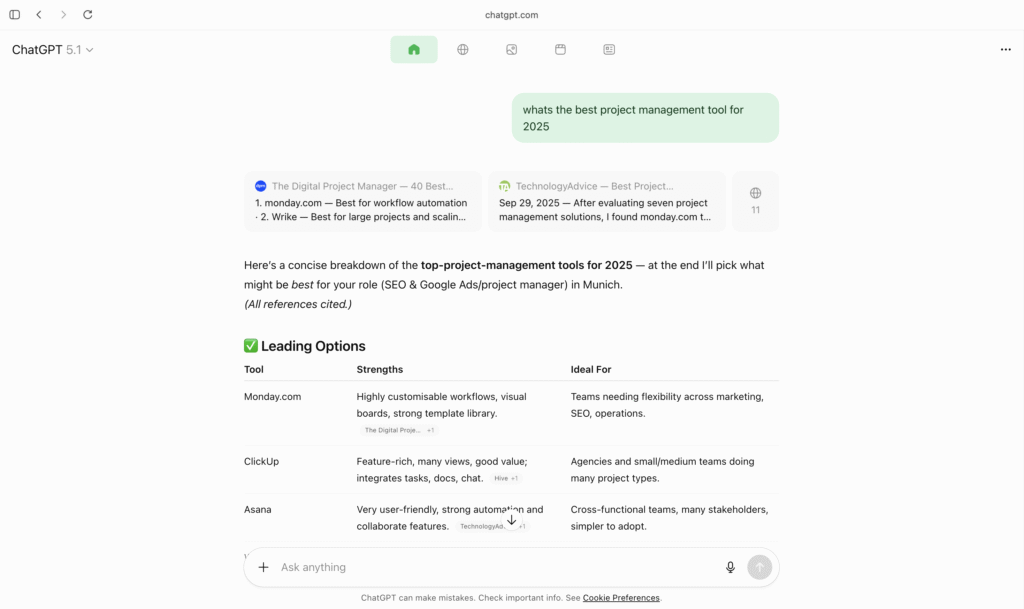
These source cards appear above the AI answer.
2. “Globe Icon” Tab = Classic Search Results (Like Google)
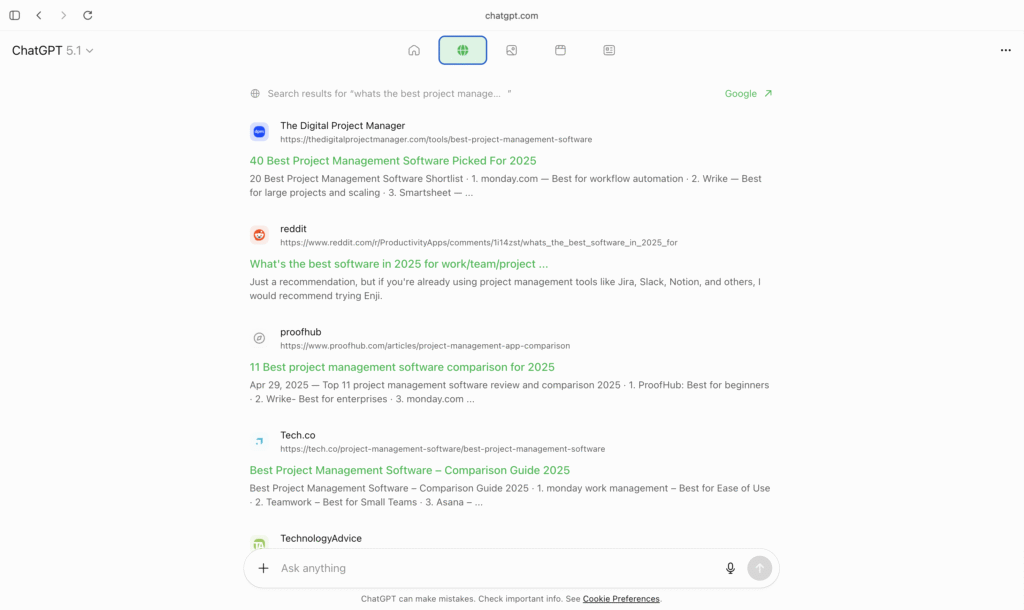
Users can tap the 🌐 Globe icon to switch to raw web search results. This feature is only available when you are using ChatGPT through Atlas browser. You will not see this feature when you use chatGPT through Google Chrome or any other browser.
This tab shows:
- Ten blue-link results
- Titles
- Meta descriptions
- URLs
- Exactly like a Google SERP
So Atlas delivers two layers of search:
3. Image, Video and News Tabs – Additional Search Layers
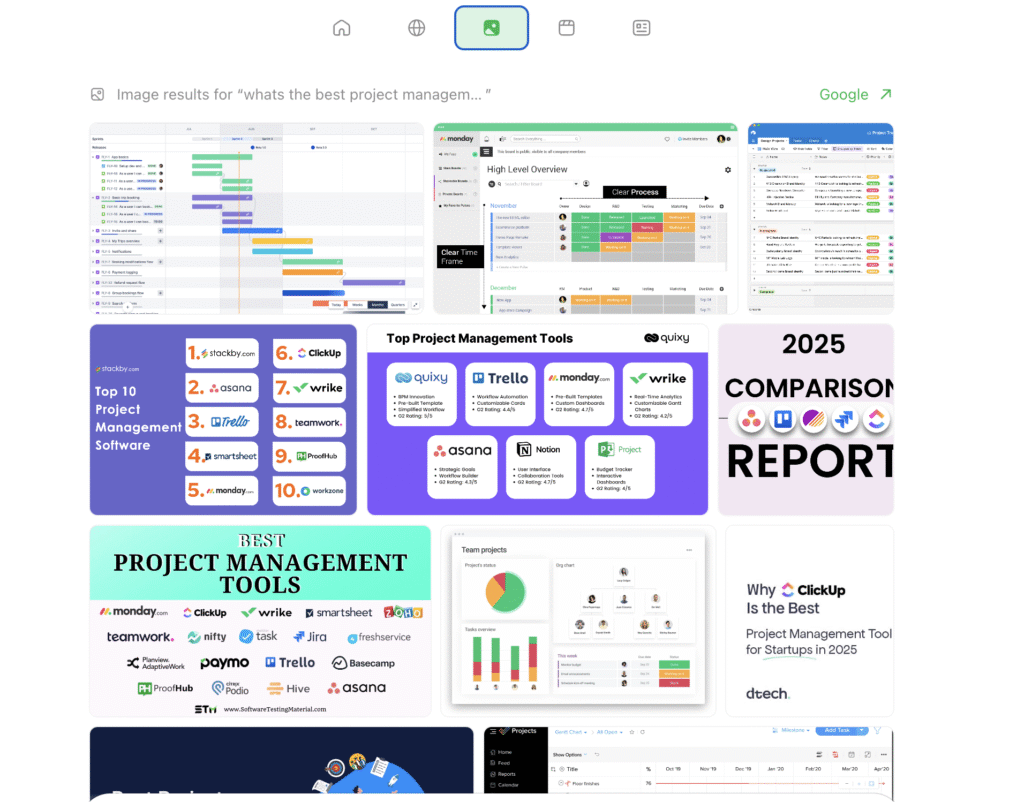
Next to the Globe icon, Atlas also provides Image, Video and News tabs, similar to Google’s vertical search options.
These tabs allow users to switch between content formats without leaving the chat:
- Image Tab: Infographics, dashboards, screenshots, comparison graphics
- Video Tab: Reviews, product demos, tutorials, walkthroughs mainly from Youtube
- News Tab: Latest announcements, industry updates, product news
Together, these layers make Atlas feel like a complete search engine, not just an AI assistant.
Why This Matters for SEO Professionals
1. Atlas Is Becoming a New “Referrer Type”
Expect to see more sessions from the below two user agents in your server logs:
ChatGPT%20Atlas/2025xxxx CFNetwork/xxxx.x Darwin/xx.x.xMozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_3) AppleWebKit/123.45 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/142.0.0.0 Safari/537.36Its not clear yet what’s the role of the first one. However, the second one signifies real users viewing your site inside ChatGPT Atlas browser.
2. AI-Driven Summaries Equal New Competition for SERP Visibility
Atlas directly summarises your content similar to chatGPT but the responses may vary.
Structured content, Q&A formatting and clear headings increase the chance of being selected as a cited source.
3. Content Must Be AI-Readable and Human-Readable
Atlas does both:
- Summarises your page
- Shows raw search results
- Displays visual and news layers
Your optimisation strategy must therefore serve all layers:
- AI summaries
- Web results
- Images
- Videos
- News
Clean content structuring, internal linking and topical depth are now essential.
Source: https://openai.com/index/introducing-chatgpt-atlas/
Thanks for reading this Article!